
What say I master Lagrangian Mechanics before I attempt this? :p
Saturday, July 26, 2008
Double Pendulum
Monday, July 21, 2008
Complex Power


But here’s another problem; we know that:



Go figure!
------------------------
Well, the answer actually is very simple: you just have to define the allowed values of the argument that define the imaginary number i, such that it can be placed to the power of something. :)
Oh yeah, this answer was contributed by Kenneth Tay Jingyi!
Friday, July 18, 2008
Expansion Woes
 And I wonder... Mmhmm...
And I wonder... Mmhmm... Thursday, July 17, 2008
A Light Burden
Assuming that the Sun is a perfect sphere, of radius R = 695 500 km and that it is a perfect blackbody with emissivity e = 1.00, and a roughly constant surface temperature of T = 5 778 K, we can use the Stefan-Boltzmann Law to determine the power of radiation emitted by the sun:

Where σ is the Stefan Boltzmann constant and A is the surface area of the Sun. And yes I've conveniently assumed the Earth is of so a low temperature with respect to the Sun such that it hardly radiates back any radiation back to the Sun.
Let us denote the distance of the Earth from the sun to be d (which is an enormous d = 149 600 000 km) and its radius as r = 6371 km. With these figures, we can then determine the intensity of solar light received at the position of our Earth, which is the initial power emitted by the Sun divided by the surface area of a sphere of radius d since the light from the Sun is isotropic in all directions:

Since all light rays coming from such a far off source will be parallel to one another, we can take the cross sectional area of the Earth to be the area that intercepts the light rays, which can be taken to be:

The power intercepted by the Earth is therefore:
Now, we know that for electromagnetic radiation, pc = E, where p is the equivalent momentum of a quantum of energy, c is the speed of light in a vacuum, and E is the energy of radiation considered. This simply means that the power is related to the momentum as such:

Don't forget, we know that the force exerted by the radiation on Earth is equivalent to the rate of change of momentum of the radiation photons (of course, we're assuming all radiation is absorbed, which is an approximation!), and thus the force exerted on Earth by the Sun's light is:


And this force is about 10^8 N! Which turns out to be an astronomical number! :) So why do you think the Earth is not being pushed away by the Sun? Easy, there's still the force of gravity, which when worked out by Newton's Law of Gravitation:

And this amounts to about 10^22 N! Do you see the difference in the two forces? The gravitational force far outweighs the force exerted by light, and thus continues to aid us in our journey through intergalactic space! :)
Wednesday, July 16, 2008
Infinity, Or Not?

As always, click the above comic strip to enlarge it; you'll notice that there's a really peculiar question which involves an infinite 2 dimensional array of resistors. Haha. Anyone game for this one? :p It's solvable!
Well, I was thinking of Kirchoff's Laws as a possible way of solving this, so let me just direct you through my methodology first.
Oh yes, a simple application of Kirchoff's Laws won't work in this question - I'll explain why later.
You start off with a single point in this infinite array and reconstruct the infinite array from scratch - let us assume we have this point (0, 0) that is the origin. We pump in 1A of current into this origin, and thus from this origin, we have four current vectors as such, coming out as shown below.

It should make sense to you that the current is divided equally into four, because all four paths are of equal resistance. We're taking one black line to be 1/4 A of current. Now, we then extend the network as such:

Notice that now each blue line is 1/12 A of current, because at each junction there are 3 paths of equal resistance. We can go on and extend the network and you'll see this:

Each red line is now worth 1/12 A of current as well! Surprise, surprise! This is because you've two '1/12 A' currents going into one junction, and then leaving into two junctions of equal resistance. It should then make sense that the two paths of red carry 1/12 A each.
So let's view our small portion in the infinite array of resistors:

Notice that in order to get from point O to point A, you go from one black to one blue to one red, and you experience a potential drop of:
And this method will only get us the potential drop between these two points, and nothing else.
Why? You might be thinking that as in the cube resistor problem in the previous post, we can simply divide the potential drop by the current to obtain the resistance between these two points. But this problem doesn't allow for that, because the initial current was 1 A, and the final current we dealt with at point A isn't 1 A but 1/12 A. This means we can no longer divide the potential drop by the initial current to obtain the equivalent resistance.
The previous problem has the starting current and end current being the same value, since by Kirchoff's First Law we know that all current going into a junction must equal all current going out of the junction if there is to be no buildup of charge.
I guess this post is another fiasco! :(
The Cube of Resistance
Envision a cube of resistors as below, where there are twelve resistors, all of the same resistance value:

Please find the resistance between points A and H (Oh yes, I took the above figure from this PDF file at www.radioelectronicschool.net, because I couldn't really be bothered to draw so much anymore, it's killing my eyes and finger dexterity, haha.)
There's more than one way of doing it, but personally, I prefer one method over the other. So... I shall just leave this here while I go for lunch. You can go figure!
2nd Round

This is the second question of the 1st IPhO - try it for kicks! (Click on it to view the enlarged picture - same for all other pictures in this post!)

Obviously the resistance here is just the simple sum of two resistors in series:

Let’s continue to add two more resistors; notice that I’ve renamed one of the resistors x (you’ll know why in a second!):
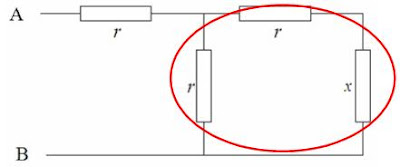
This is a little trickier; the resistance here must take into account the parallel circuitry, which I’ve circled out in red. If you can’t see this, well, let me redraw it in a more accessible manner:

And of course, if you still remember the formula for parallel resistors, this new set-up has a fairly easy to calculate expression for its resistance:

And then let’s do one more addition of a branch to see how everything adds up, to understand how I’m going to simplify the situation:

Well, without redrawing it, I’d expect you to say that the set-up now consists of two parallel set-ups. For those who can’t see yet, I’ve tried to point out using circles again. Look above at the blue circle; I can represent this as a resistor x, and then the diagram is simplified into:

And what do you notice? Haha, we’ve already obtained the resistance for this, which was determined earlier to be:

So what’s x? Well, let’s find out; referring to the blue circle, I see that x’s resistance is simply equivalent to a set of parallel resistors:

Okay, so that you’ve roughly got my trick of simplifying, let’s do a long set so that you’ll be seeing what I’m seeing:

Let’s do the red circle first, and let’s call this new resistor a:

Now, treating the red circle as a resistor a, we can simplify the diagram into:

Alright, so now let’s do the blue circle and let’s call this new resistor b:

So now we can simplify again:

And now let’s do the green circle and let’s call this resistor c:

And now, let’s simplify again:

This couldn’t be simpler, and let’s do the orange circle this time and call it a resistor d, and find its resistance:

With this, we can then simplify our diagram as:

And the overall resistance is therefore simply:

Now, if you haven’t seen or noticed the pattern yet, let me just write out everything in full:

What a monster! You may want to view it in full size, haha. Notice that there is a repeating unit! And if the series goes on and on indefinitely, let me just re-write it in a more digestible way:

Can you spot the repeating unit yet? Haha. If you haven’t spotted the recurring unit yet, it’s simply this monster right here:

But what is this creature? Notice that the overall resistance R is just the repeating unit:

So how do we solve this thing? Well, algebra gives us a good method:

And then now we manipulate this expression into a quadratic equation, as such, to obtain R:

Which can then be solved using the standard quadratic equation (notice I’ve rejected the negative answer since no resistance is negative):

And as some of you might have already noticed, the Golden Ratio (phi) appears in the answer:

Such that:

Well, what is the Golden Ratio? Let’s leave that for another entry, because I’m absolutely tired of typing out equations and expressions for the day. I’ll give a hint though; recall the Fibonacci sequence as:

If you look closely, each succeeding term is obtained via addition of its two preceding terms. Well, if you take any term and divide it by its preceding term, you’ll obtain a number close to the Golden Ratio (phi). Let’s say we take 89 and 55:

And this ratio gets increasingly closer to the Golden Ratio as one continues on into the series.
And wow! What a lengthy post! And it's rather strange isn't it? Then adding more and more resistors forces your resistance into a fixed, finite value instead of an infinite resistance, and the fact that the Golden Ratio pops up in such an instance! Simply amazing! :p
